NASA
NASA Names Companies to Develop Human Landers for Artemis Moon Missions (Press Release)
NASA has selected three U.S. companies to design and develop human landing systems (HLS) for the agency’s Artemis program, one of which will land the first woman and next man on the surface of the Moon by 2024. NASA is on track for sustainable human exploration of the Moon for the first time in history.
The human landing system awards under the Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP-2) Appendix H Broad Agency Announcement (BAA) are firm-fixed price, milestone-based contracts. The total combined value for all awarded contracts is $967 million for the 10-month base period.
The following companies were selected to design and build human landing systems:
- Blue Origin of Kent, Washington, is developing the Integrated Lander Vehicle (ILV) – a three-stage lander to be launched on its own New Glenn Rocket System and ULA Vulcan launch system.
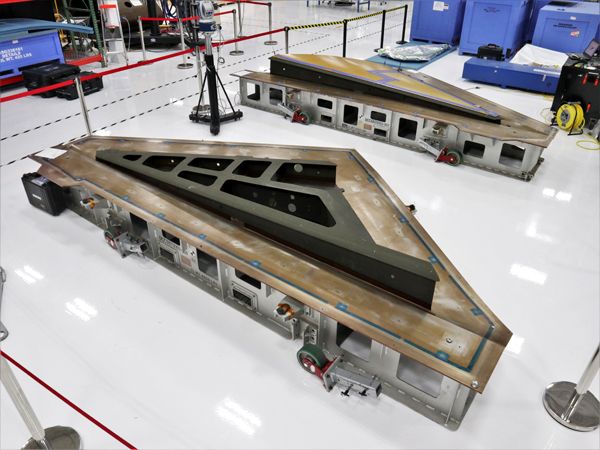
- Dynetics (a Leidos company) of Huntsville, Alabama, is developing the Dynetics Human Landing System (DHLS) – a single structure providing the ascent and descent capabilities that will launch on the ULA Vulcan launch system.
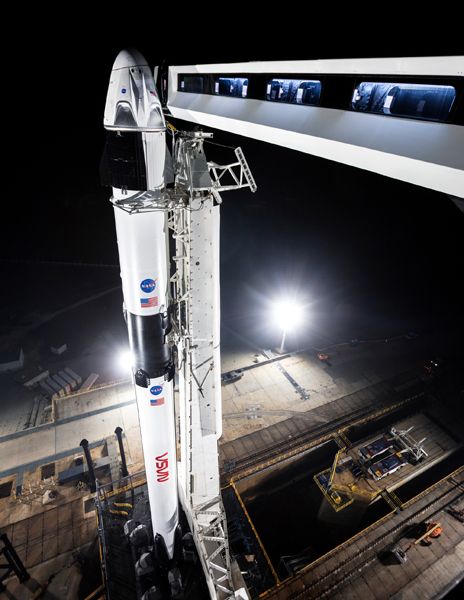
- SpaceX of Hawthorne, California, is developing the Starship – a fully integrated lander that will use the SpaceX Super Heavy rocket.
“With these contract awards, America is moving forward with the final step needed to land astronauts on the Moon by 2024, including the incredible moment when we will see the first woman set foot on the lunar surface,” said NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine. “This is the first time since the Apollo era that NASA has direct funding for a human landing system, and now we have companies on contract to do the work for the Artemis program.”
Fifty years ago, NASA’s Apollo Program proved it is possible to land humans on the Moon and return them safely to Earth. When NASA returns to the Moon in four years with the Artemis program, it will go in a way that reflects the world today – with government, industry, and international partners in a global effort to build and test the systems needed for challenging missions to Mars and beyond.
“We are on our way.” said Douglas Loverro, NASA’s associate administrator for Human Explorations and Operations Mission Directorate in Washington. “With these awards we begin an exciting partnership with the best of industry to accomplish the nation’s goals. We have much work ahead, especially over these next critical 10 months. I have high confidence that working with these teammates, we will succeed.”
NASA’s commercial partners will refine their lander concepts through the contract base period ending in February 2021. During that time, the agency will evaluate which of the contractors will perform initial demonstration missions. NASA will later select firms for development and maturation of sustainable lander systems followed by sustainable demonstration missions. NASA intends to procure transportation to the lunar surface as commercial space transportation services after these demonstrations are complete. During each phase of development, NASA and its partners will use critical lessons from earlier phases to hone the final concepts that will be used for future lunar commercial services.
"I am confident in NASA’s partnership with these companies to help achieve the Artemis mission and develop the human landing system returning us to the Moon" said Lisa Watson-Morgan, HLS program manager at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. "We have a history of proven lunar technical expertise and capabilities at Marshall and across NASA that will pave the way for our efforts to quickly and safely land humans on the Moon in 2024.”
NASA experts will work closely with the commercial partners building the next human landing systems, leveraging decades of human spaceflight experience and the speed of the commercial sector to achieve a Moon landing in 2024.
The HLS program manager will assign NASA personnel to support the work of each contractor, providing direct, in-line expertise to the companies as requested in their proposals (e.g., design support, analysis, testing). The HLS program will also perform advanced development and risk reduction activities, working in parallel to better inform the approach for the 2024 mission and the necessary maturation of systems for the future sustaining architecture.
Charged with returning to the Moon in the next four years, NASA’s Artemis program will reveal new knowledge about the Moon, Earth, and our origins in the solar system. The human landing system is a vital part of NASA’s deep space exploration plans, along with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket, Orion spacecraft, and Gateway.
NASA is returning to the Moon for scientific discovery, economic benefits, and inspiration for a new generation. Working with its partners throughout the Artemis program, the agency will fine-tune precision landing technologies and develop new mobility capabilities that allow robots and crew to travel greater distances and explore new regions of the Moon. On the surface, the agency has proposed building a new habitat and rovers, testing new power systems and much more to get ready for human exploration of Mars.
****

Dynetics / SpaceX / Blue Origin